The background
What is rheumatoid arthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic, inflammatory autoimmune disease. It primarily affects the small joints of the hands and feet, causing pain, swelling and stiffness.[1] As it progresses, RA can affect any bodily system and is associated with several complications and other health conditions, including cardiovascular disease and osteoporosis.[2] RA can be life-changing, with its debilitating effects meaning some affected people have difficulty completing daily tasks.1 People with RA also have an increased risk of premature death.[2]
Prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis
RA is common in the UK with a prevalence of around 1%. People may develop the condition at any age, with a peak onset at 30-50 years of age. Women are between two and four times more likely to have RA than men.[2]
NHS and wider economic costs of rheumatoid arthritis
RA is a condition that has significant health-economic consequences.[3] In 2012, the fourth largest area of NHS budget spend in England was on musculoskeletal conditions (4.7%), including RA. In 2017, the estimated shared health costs of RA and osteoarthritis across the UK was £10.2 billion.[4]
Approximately one-third of people stop work within 2 years of being diagnosed with RA, and half within 10 years. Aside from the significant direct costs to NHS, this leads to even larger indirect costs to the UK economy. In 2009/10 the indirect economic costs were estimated to be between £1.8 and £8 billion per annum.[3]
The challenge
The National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) Quality standard for rheumatoid arthritis in over 16s states that “Adults with rheumatoid arthritis are given opportunities throughout the course of their disease to take part in educational activities that support self-management.”[5]
Around 50% of people with chronic conditions such as RA do not adhere to long-term medication,6-8 leading to increased adverse health outcomes[6] and stretching NHS resources.[7] The World Health Organization (WHO) states that “Increasing the effectiveness of adherence interventions may have a far greater impact on the health of the population than any improvement in specific medical treatments”.[8]
Cambridge Arthritis Research Endeavour (CARE) approached Cognitant to help them improve the support given to people with RA who are about to start on biological and targeted disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs). Supported by arm’s length educational grants from two pharmaceutical companies, they sought to empower patients with information about what RA is and how the treatments work. The aim was to support shared decision-making and therefore reduce strain on the NHS by streamlining and improving the quality of consultations.
The solution
In partnership with CARE, Cognitant co-created an immersive, avatar-led educational module for people with RA about to start on biologic therapy. The module is viewable in interactive video format, as well as with a virtual reality (VR) headset. Patients have access to an explanation of the disease process, and the mode of action of biological and targeted DMARDs. It features a 360-degree video of an injection demo, and a series of infographics and virtual objects to aid knowledge retention.

Why an immersive approach was taken
Traditional healthcare communication methods, such as printed materials, may have limited beneficial effects on patient outcomes.9 Visual, interactive content has the power to improve patient self-management and health outcomes, and has proven to be successful, potentially due to increased immersion and therefore improved engagement.[9,10]
Education provided by digital avatars has the ability to improve patient knowledge and self-care behaviours in chronic diseases.[10] Viewing health educational information with virtual goggles has previously been shown to improve medication adherence in HIV,[11] allowing viewers to create ‘memory palaces’ and increasing fact recall.[12]
The results
The programme was piloted at Addenbrooke’s Hospital, beginning in June 2020, and at Norfolk and Norwich University Hospital (NNUH), beginning in September 2020.
As of February 2023, combined data for both sites demonstrated positive engagement, with 252 unique users accessing the programme a total of 336 times, at a rate of 1.3 visits per user. The average time spent per session was 16 minutes 9 seconds.
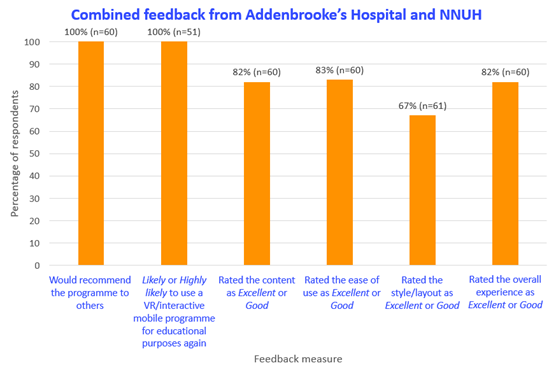
User feedback was also collated across the two sites, with 100% of respondents saying they would recommend the interactive programme to others. The content, ease of use and overall experience were all rated as ‘Excellent’ or ‘Good’ by >80% of respondents.
The feedback from the NNUH pilot showed that only 12% of users (N=52) rated their knowledge of biological and targeted DMARDs as ‘Good’ or ‘Excellent’ prior to using the programme, with this rate rising to 63% post-engagement (N=48). This was reflected in the feedback from the Addenbrooke’s pilot, where 86% of respondents felt that they knew more about DMARDs after using the programme (N=7).
Testimonial
“Cognitant’s interactive educational program has changed the way that we deliver our service in Norwich by providing an engaging, informative resource that has helped us to streamline the educational offering for our patients. Previously, our specialist nursing team provided two education appointments with biologic-naïve patients being initiated on a biological treatment. Use of the interactive RA program allowed us to free up one of these appointments, which, given pressures on our service, has been hugely valuable.
Through continuous evaluation with patients, we have seen high levels of engagement and patient-reported improvements in their understanding of treatments. Overall, we have seen the strong utility of interactive educational approaches like Cognitant’s RA program in supporting our patients with understanding of their disease and treatments.”
Dr Jordan Tsigarides, Senior Clinical Fellow (Rheumatology) and VR Faculty Lead for Postgraduate Education, NNUH
References
- NHS. Rheumatoid arthritis. Available at: https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed September 2023
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) Clinical Knowledge Summary. Rheumatoid arthritis. Available at: https://cks.nice.org.uk/topics/rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed September 2023
- Bowman SJ et al. The national clinical audit for rheumatoid and early inflammatory arthritis. Clin Med (Lond) 2016;16(6):500-1
- Versus Arthritis. Representation to the budget, January 2021. Available at: https://www.versusarthritis.org/media/23185/representation-to-the-budget-jan-21.pdf. Accessed September 2023
- NICE Quality standard. Rheumatoid arthritis in over 16s (QS33). Available at: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/qs33. Accessed September 2023
- Lee JK et al. Effect of a pharmacy care program on medication adherence and persistence, blood pressure, and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2006;296(21):2563-71
- Royal Pharmaceutical Society. Medicines optimisation: helping patients to make the most of medicines. Available at: https://www.rpharms.com/Portals/0/RPS%20document%20library/Open%20access/Policy/helping-patients-make-the-most-of-their-medicines.pdf. Accessed September 2023
- World Health Organization. Adherence to long-term therapies: evidence for action. Available at: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/42682. Accessed September 2023
- Wonggom P et al. Effectiveness of using avatar-based technology in patient education for the improvement of chronic disease knowledge and self-care behavior: a systematic review protocol. JBI 2016;14(9):3-14
- Wonggom P et al. Effectiveness of avatar-based technology in patient education for improving chronic disease knowledge and self-care behavior: a systematic review. JBI 2019;17(6):1101-29
- Liran O et al. Using virtual reality to improve antiretroviral therapy adherence in the treatment of HIV: open-label repeated measure study. Interact J Med Res 2019;8(2):e13698
- Krokos E et al. Virtual memory palaces: immersion aids recall. Virtual Reality 2019;23(1):1-15
Cognitant
Looking to empower people with health information for better patient outcomes?
Additional Case Studies
Co-Creating a Personalised Digital Storybook for Children with Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome (aHUS)
June, 2025
Challenge Atypical Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome (aHUS) is a rare, life-threatening disease characterised by blood clots forming in small vessels, leading to kidney failure, anaemia, and...
Asthma Essentials
January, 2025
[embed]https://youtu.be/qmeiwjCr9Go[/embed] The challenge: Asthma remains a major health concern in the UK, affecting 5.4 million people, including 1.1 million children. Each year, the condition leads...
Cognitant successfully streamlines a top 10 pharma Patient Support Programme
July, 2024
A top 10 pharma company challenged Cognitant to optimise their Patient Support Programme (PSP) for an injectable medication, with the aim to streamline approvals, save...